For adults with dysphagia not caused by a stroke there is insufficient evidence on efficacy to support the use of this procedure.
Nice guidelines electrical stimulation dysphagia.
19 december 2018 register an interest.
This guidance replaces nice interventional procedures guidance on transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia ipg490.
Swallowing therapy uses exercises to improve muscle function.
Nice has identified relevant audit criteria and has developed an audit tool which is for use at local discretion.
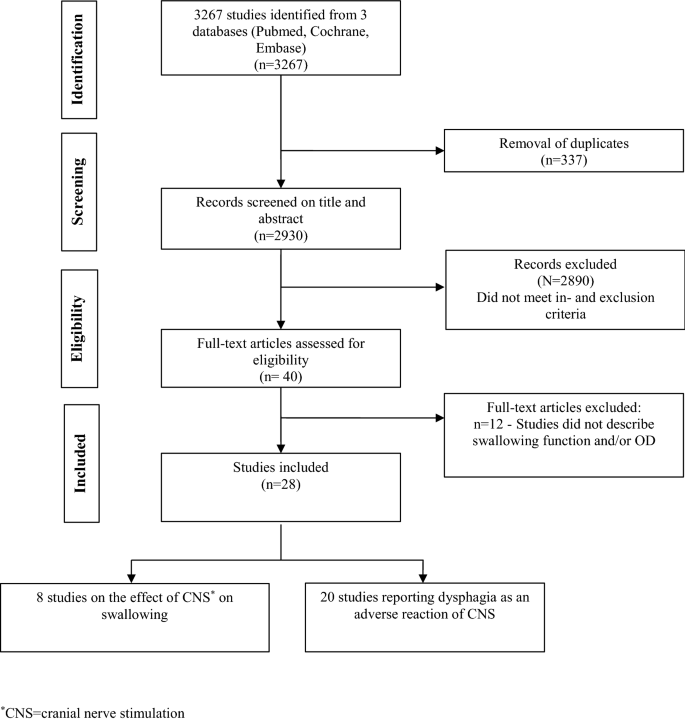
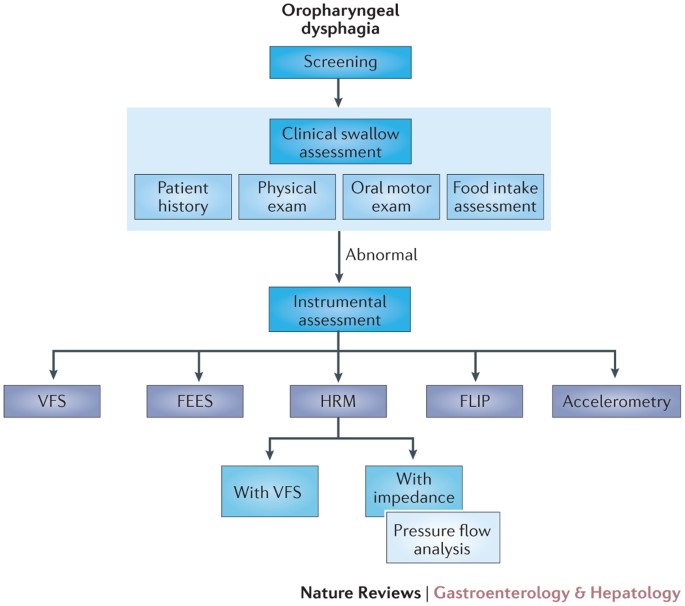
Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation nmes in december 2018 the national institute for health and care excellence nice issued guidance to the nhs in england wales and northern ireland on one group of electrical stimulation interventions.
Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults.
In addition the use of nice s information for the public is recommended.
Further research on transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults should address patient selection variations.
Transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults interventional procedures guidance ipg634 published date.
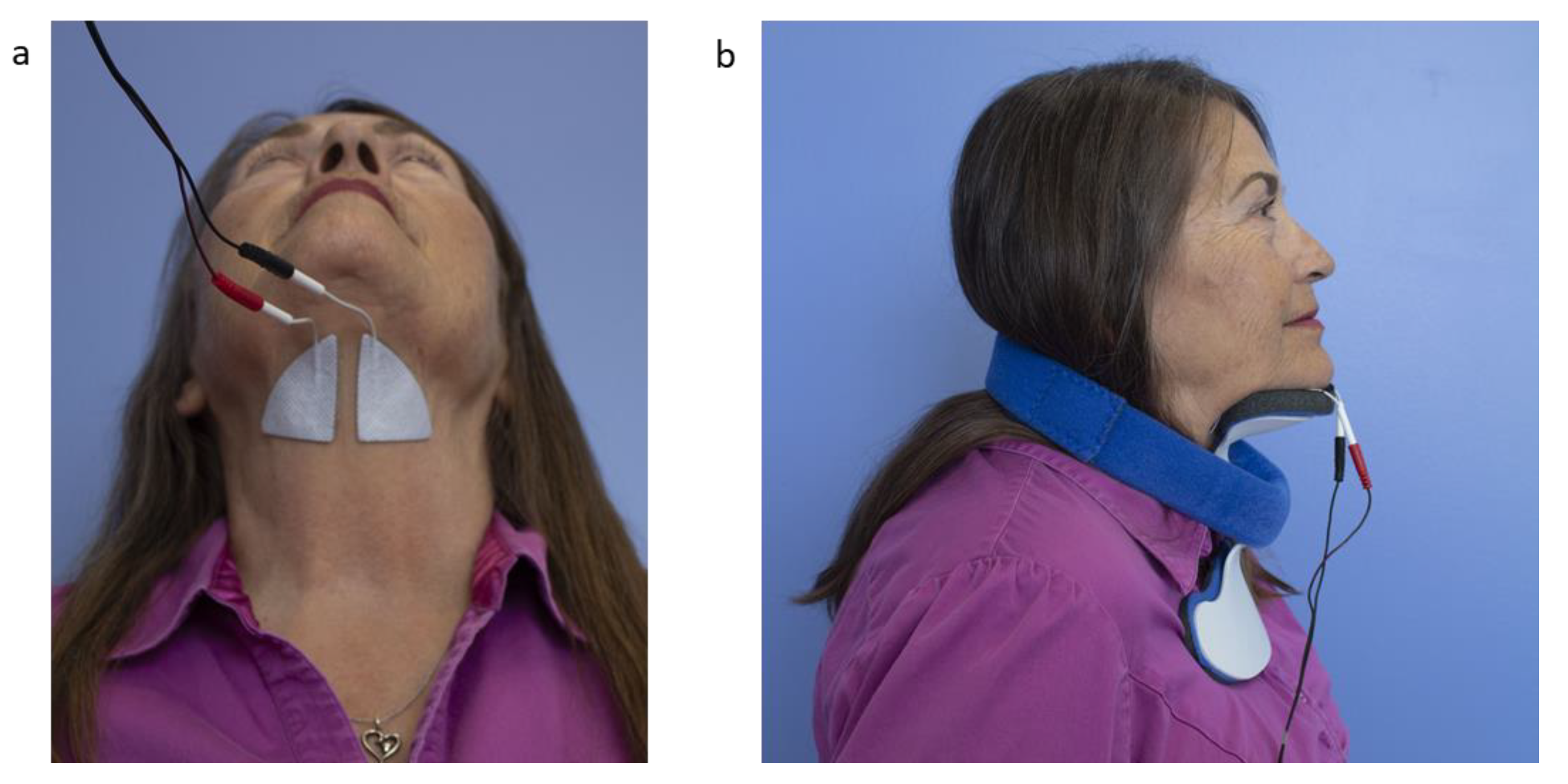
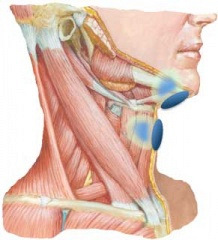
The aim of nmes is to increase the effectiveness of swallowing therapy by strengthening the muscles involved in swallowing.
2 3 transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation nmes is usually used as well as traditional swallowing therapy for treating oropharyngeal dysphagia.
Current evidence on transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults shows there are no major safety concerns.
Audit and review clinical outcomes of all patients having transcutaneous neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia.
Your responsibility this guidance represents the view of nice arrived at after careful consideration of the evidence available.
The full overview document from nice with review of relevant studies.
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for oropharyngeal dysphagia.
For adults with dysphagia after a stroke the evidence on efficacy suggests a potential benefit but is limited in quality and quantity.